USTC Institute of Nuclear Medical Physics Collaborates with First Affiliated Hospital to Publish Patient-Specific CT Dose Big Data Study in Medical Physics Journal
The Institute of Nuclear Medical Physics at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has collaborated with the First Affiliated Hospital to publish a groundbreaking paper in the Medical Physics journal. Titled "Uncertainty Quantification for CT Dosimetry Based on 10,281 Subjects Using Automatic Image Segmentation and Fast Monte Carlo Calculations," the paper marks an advancement in CT dose big data analysis and uncertainty quantification. The study, published online in April 2025, was led by Zirui Ye, a PhD candidate under the supervision of Prof. Xie George Xu, who is the corresponding author.
CT scans are one of the primary sources of medical radiation exposure worldwide. Traditional dose estimation methods rely on simplified models and population-averaged data, which struggle to accurately quantify dose uncertainties arising from inter-individual anatomical differences. The research team developed a software platform integrating automatic image segmentation and GPU-accelerated Monte Carlo (MC) calculations, achieving the first-ever uncertainty quantification of CT doses based on over 10,000 cases.
The research results indicate that traditional linear fitting methods showed maximum absolute errors of up to 4.51 mGy/CTDIvol, with relative errors exceeding 50%, highlighting the necessity of patient-specific dose estimation. Statistical analysis showed that small sample datasets tend to underestimate the range of organ dose variations, and the uncertainty decreases as the sample size increases. This methodology can be used for large-scale CT dose data mining and trend prediction, supporting radiation risk epidemiology studies and quality control.
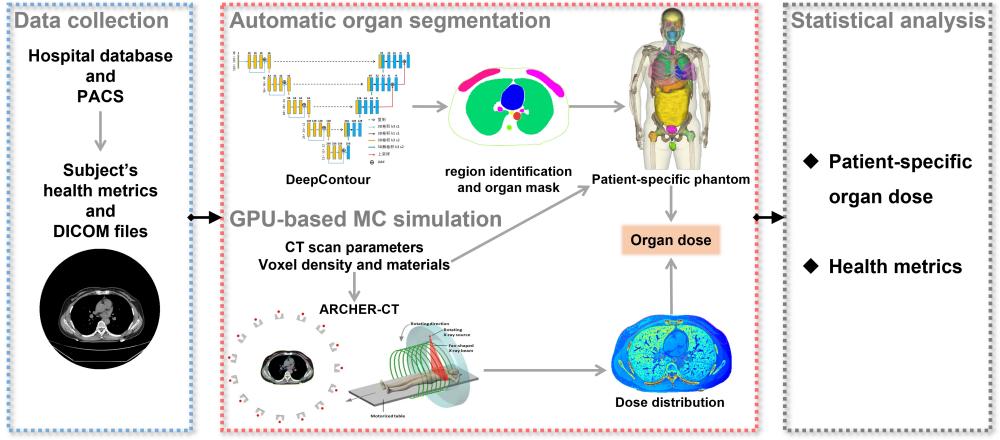
Figure 1: Workflow for patient-specific CT dose calculation, including data collection, automatic segmentation, fast MC simulation, and statistical analysis. The whole calculation processes for the 10,281 cases were completed in just 16 days using a single NVIDIA RTX 3080 GPU card.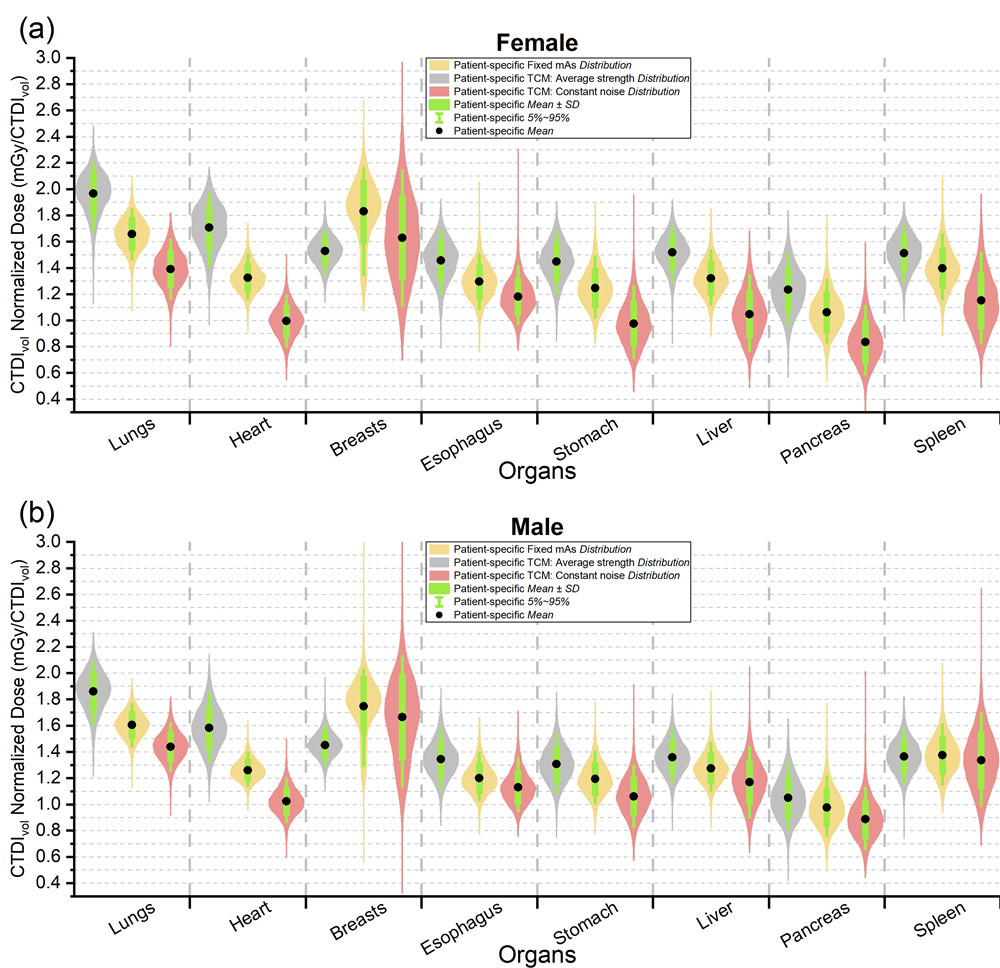
Figure 2: Comparison of organ dose distributions per CTDIvol under fixed and modulated tube current modes.
Full paper link: https://aapm.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/mp.17796

