Paper on Virtual Source Models Published in the Medical Physics Journal
On September 27, 2024, the Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, the Institute of Nuclear Medical Physics of University of Science and Technology of China and Wisdom Technology have published a paper titled An automated commissioning method based on virtual source models: Customizing Monte Carlo dose verification models for individual accelerators in the Medical Physics. Bo Cheng (Institute of Nuclear Medical Physics of USTC) and Yuan Xu (Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences) are joint first authors. The paper’s coauthors include Jianrong Dai from the Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Professor George XU, Eric Pei and Alex Ren from Wisdom Technology Company.
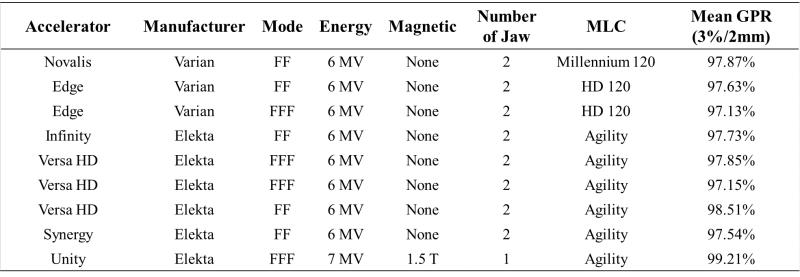
Based on the "three-source model" virtual source, this paper implements an accelerator automatic modelling method. First, the existing virtual source method is improved, a new flattening filter is proposed and the sampling method of the particle source is modified. Then, three sets of objective functions are designed to represent the differences between the Monte Carlo simulation values and the measured values. The corresponding virtual source parameters are set for each set of objective functions, and specific step functions, advancing direction and iteration priority are designed for each iteration parameter. Based on this, an automatic optimization process is designed, which can automatically adjust the virtual source model without any human intervention. The proposed automatic modelling method is applied to the modelling work of 9 accelerators, the average gamma passing rates (3%/2mm) for ArcCHECK measurements in QA plans are all higher than 97%, indicating the accuracy of the accelerator modeling method. Taking the MR-guided accelerator Unity as an example, the automatic modelling method is compared with the manual adjustment method of "accelerator model parameters" and both methods have a high agreement with the measured values. The average gamma passing rates (3%/2 mm) for manual modelling and automatic modelling are 99.36% ±1.28% and 99.21% ±1.03%, respectively. There is no statistically significant difference between the two gamma passing rates (p=0.282). This automatic modelling method combined with a Monte Carlo dose calculation engine provides a fast dose verification method that can customize a model for each accelerator.
Table Gamma passing rate between ArcherQA calculated results and ArcCHECK measured values
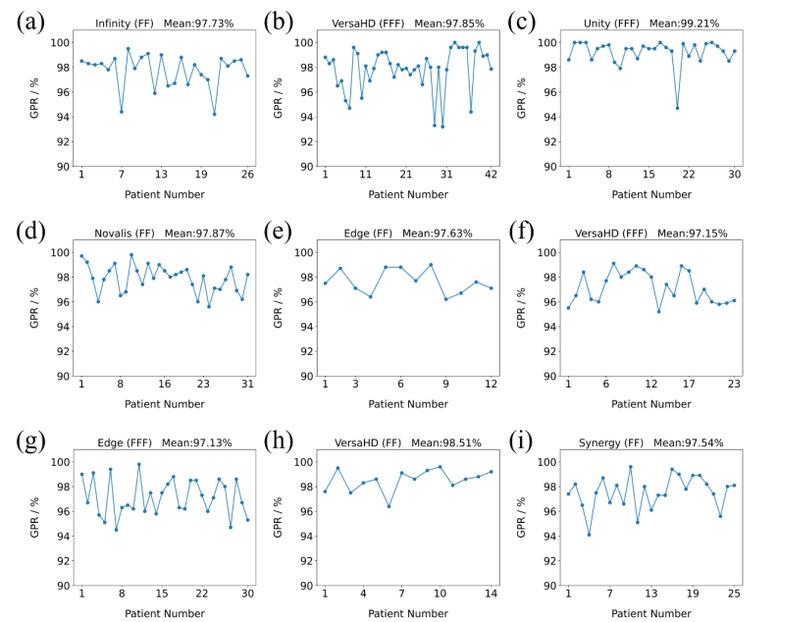
The upper figure shows the gamma pass rate between ArcherQA dose and ArcCHECK measurement in the clinical QA plan. (a-i) represent the gamma pass rates obtained from different accelerators, with the accelerator model, flattening filter or flattening filter-free and the average gamma pass rate in the clinical QA plan are indicated above each subgraph.
Note: The accelerator modelling mainly refers to the particle distribution above the jaw. The simulation of the jaw uses the self-developed collimator model and the in-vivo dose calculation uses the GPU-accelerated Monte Carlo dose calculation engine ArcherRT.
Whether in academic research or product research and development, Wisdom Technology will continue to work better. Moving forward, we will continue to strengthen collaborations with domestic and international peers, driving advancements in radiotherapy technology to provide cancer patients with more precise and effective treatment solutions.
The paper link: https://aapm.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mp.17418

