Paper on Monte Carlo Simulations for MRI Guided Proton Radiation Therapy Published in the Medical Physics Journal
On November 21, 2023, a paper titled A GPU-based fast Monte Carlo code that supports proton transport in magnetic field for radiation therapy authored by Dr. Shijun Li (first author) and Professor George XU (corresponding author) from the Institute of Nuclear Medicine Physics of University of Science and Technology of China was published in the Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics. The research work of this paper is based on Wisdom technology product ArcherQA - Independent QA Dose-Check Software.
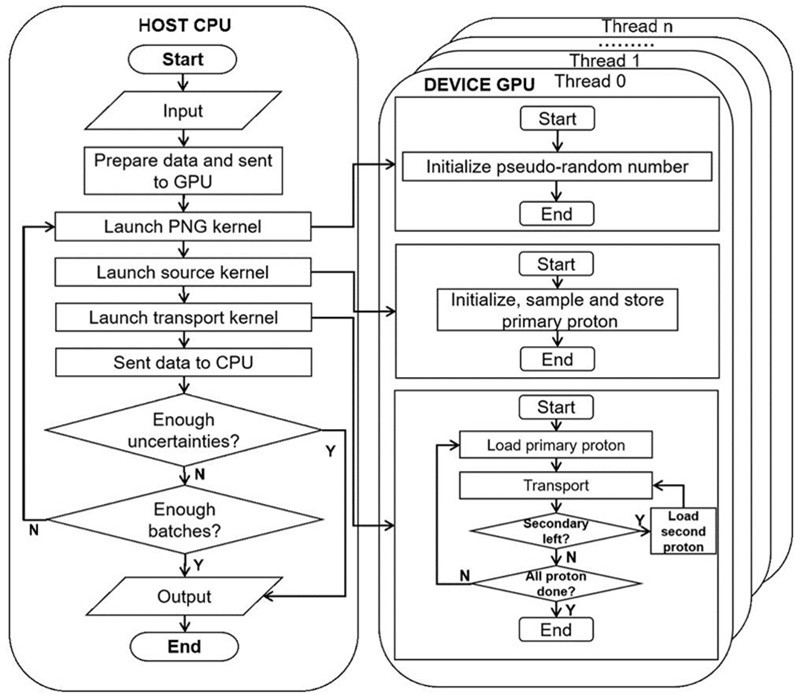
ArcherQA is an independent dose verification software with GPU-based Monte Carlo algorithms. It supports various photon radiotherapy devices and procedures and it has been used in the radiation oncology departments of several hospitals. This paper extends the computational capabilities to proton radiotherapy based on previous work. The proton transport physical modeling employs the concentrated history II class algorithm, taking into account multiple Coulomb's scattering, continuousslowing down approximation, energy straggling, electron production, nuclear elastic scattering and inelastic scattering. The GPU programming is based on the CUDA framework, using C++ language and following the typical CUDA programming model. Finally, Archer was compared and validated using the general Monte Carlo software TOPAS, which is known as the "gold standard" for radiation dose calculation in the industry, taking into account the data from the water tank to the clinical patient's radiotherapy plan. The results show that the dose distribution accuracy simulated by Archer is highly consistent with that of TOPAS, and Archer simulations each ten million primary protons in only about 3s, which is much faster than TOPAS. This paper also explores the influence of magnetic field on the dose distribution of proton therapy, for the future preliminary exploration of nuclear magnetic-guided proton radiotherapy. The results show that the Monte Carlo algorithm must be used to calculate the effect of Lorentz force on the proton beam in the presence of a magnetic field.
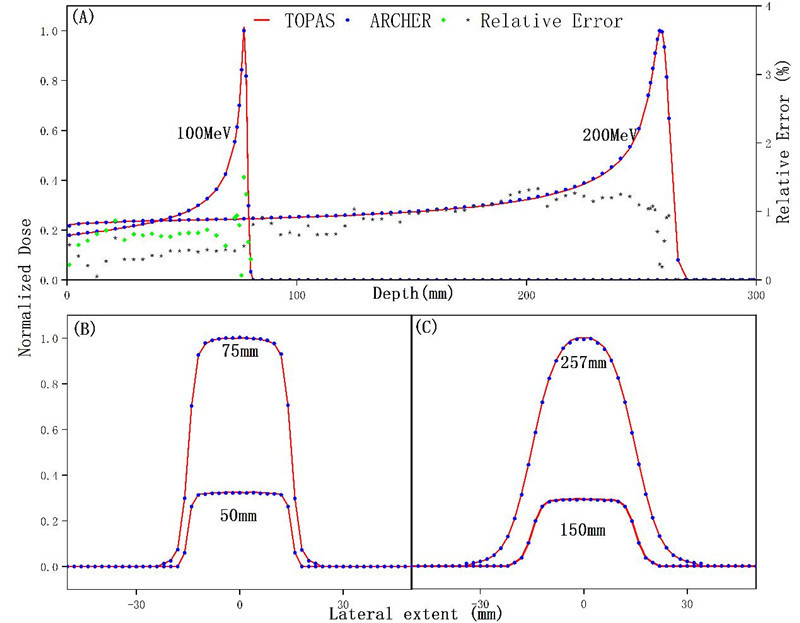
In Figure 1, the water tank verification result (A) is the comparison results of the water tank IDD curves. (B) is the comparison results of lateral dose distribution for 100MeV proton beam at different water depths. (C) is the comparison results of lateral dose distribution for 200MeV proton beam at different water depths.
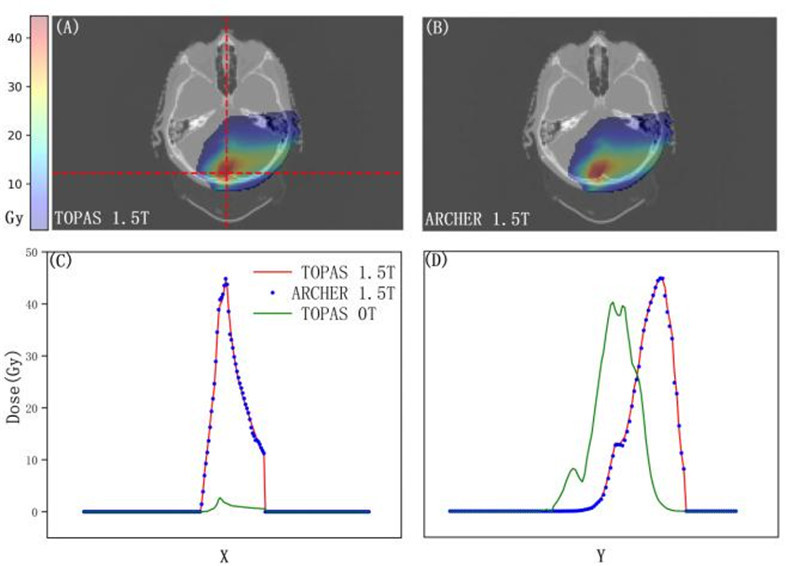
In result figure 2, due to the influence of the magnetic field on the dose, (A) and (B) show the dose distribution maps calculated by TOPAS and Archer at 1.5T magnetic field, respectively. (C) and (D) show the dose contour comparison maps corresponding to the red dashed line in figure (A).
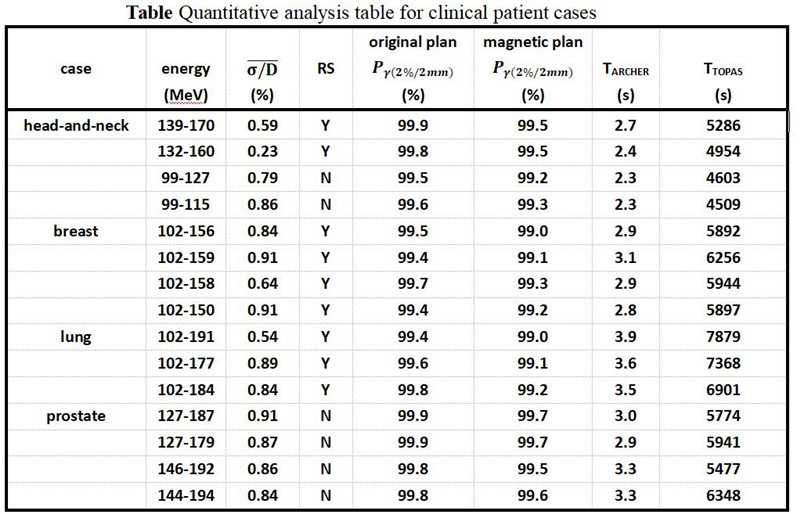
Wisdom Technology’s expert engineering team has meticulously crafted ArcherQA, which can adeptly address the daily challenges faced by clinical physicists and radiation oncologists, and greatly improving workflow efficiency.

